Welcome to Controls Traders, located in Adelaide, South Australia. We are a supplier of quality building automation controls and peripheral products for the HVAC industry. We stock a full range of controllers, sensors, valves and actuators, damper actuators and accessories to suit any application. Our aim is to provide our customers with the highest level of service, from sales to delivery and after sales support. With our extensive in-house knowledge and expertise in the industry, we can advise you on selection and application of our wide range of controls products.
Backed by 40 years industry experience. When you just need to be sure.

No, we’re serious. Anywhere. Anytime.

We stock all major global brands. And if we don’t have it, we’ll find it.

We warehouse the stock so you don’t have to wait.

$150.00 ex GST
Helpful guys over the counter, prompt responses and stock a wide variety of HVAC equipment. One of my go-to stores for parts and advise.
08/10/23
Huge range of HVAC controls readily available off the shelf with excellent customer service and knowledge amongst all staff!? If it's not on the shelf they can get it for you quick!
02/10/23
Great service, great products. The guys are always very helpful and will try to get whatever you need.
19/09/23
Have been using Control Traders for a while now. Peter and the team have been very helpful. Great prompt service
28/10/23


If you are managing a commercial building in Australia, you know that HVAC consumption typically accounts for 40–50% of your total electricity bill. For facility managers, ensuring that these systems run efficiently is critical for both occupant comfort and the bottom line.
A modern HVAC control system—often integrated into a broader Building Management System (BMS) or Building Automation System (BAS)—is the digital intelligence that runs your facility. It automates the flow of air and water, allowing your building to react to real-time demands rather than relying on manual adjustments.
At Controls Traders, we have over 40 years of industry experience supplying high-quality building automation controls across Australia. Whether you are looking to understand your current setup or planning an upgrade, here is your essential guide to how an HVAC control system works.
The Core Components of an HVAC Control System
An effective control system can be broken down into three main categories: the brain, the nervous system, and the muscles.
1. The Brains: Controllers and Thermostats
The controllers are the digital intelligence of your HVAC system. They receive data from the building, process it through programmed logic (like PID loops), and send commands to the mechanical equipment.
2. The Nervous System: Sensors
No matter how advanced your controller is, it cannot maintain efficiency if it receives inaccurate data. Sensors measure the physical environment and feed this data back to the BMS.
3. The Muscles: Actuators and Valves
Once the controller makes a decision, it needs a physical mechanism to execute it. This is where Actuators and Valvescome in.
4. The Efficiency Drivers: Variable Speed Drives (VSDs)
Older HVAC systems ran fans and pumps at 100% full speed constantly, wasting immense amounts of power. Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) act as a "dimmer switch" for your heavy motors. By slowing a fan down by just 20% to match the actual airflow demand, a VSD can reduce the fan's electricity consumption by roughly 50%.
Protecting Your Investment
Facility managers know that "uptime" is everything. Your control panels contain sensitive electronics that are highly susceptible to "dirty power" and momentary voltage sags. Integrating Industrial UPS Systems into your mechanical switchboards ensures that your BMS controllers, network hardware, and field power supplies stay online during power blips, preventing data corruption and plant room blindness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a stand-alone controller and a BMS controller? A stand-alone controller provides local control for a specific piece of equipment or zone, whereas a BMS controller integrates into a larger network (often using BACnet or Modbus) to allow centralized monitoring, logging, and remote tuning of the entire building.
How can I improve my existing HVAC energy efficiency? The fastest ways to improve efficiency are upgrading to Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) to reduce fan/pump speeds at partial loads, and installing Pressure-Independent Control Valves (PICVs) to prevent chilled water overflow. Additionally, ensuring your CO₂ sensors are correctly placed allows for intelligent Demand Control Ventilation.
Where can I buy HVAC control parts in Australia? Controls Traders is an Australian-owned business based in Stepney, South Australia. We warehouse a massive inventory of trusted global brands—including Belimo, Siemens, Schneider, and Honeywell—and offer fast delivery anywhere across Australia.
Need to replace a faulty part or upgrade your facility's controls? With over 40 years of combined HVAC and automation expertise, our team is ready to help. Request a quote online or call us today on 1300 740 140
Read more

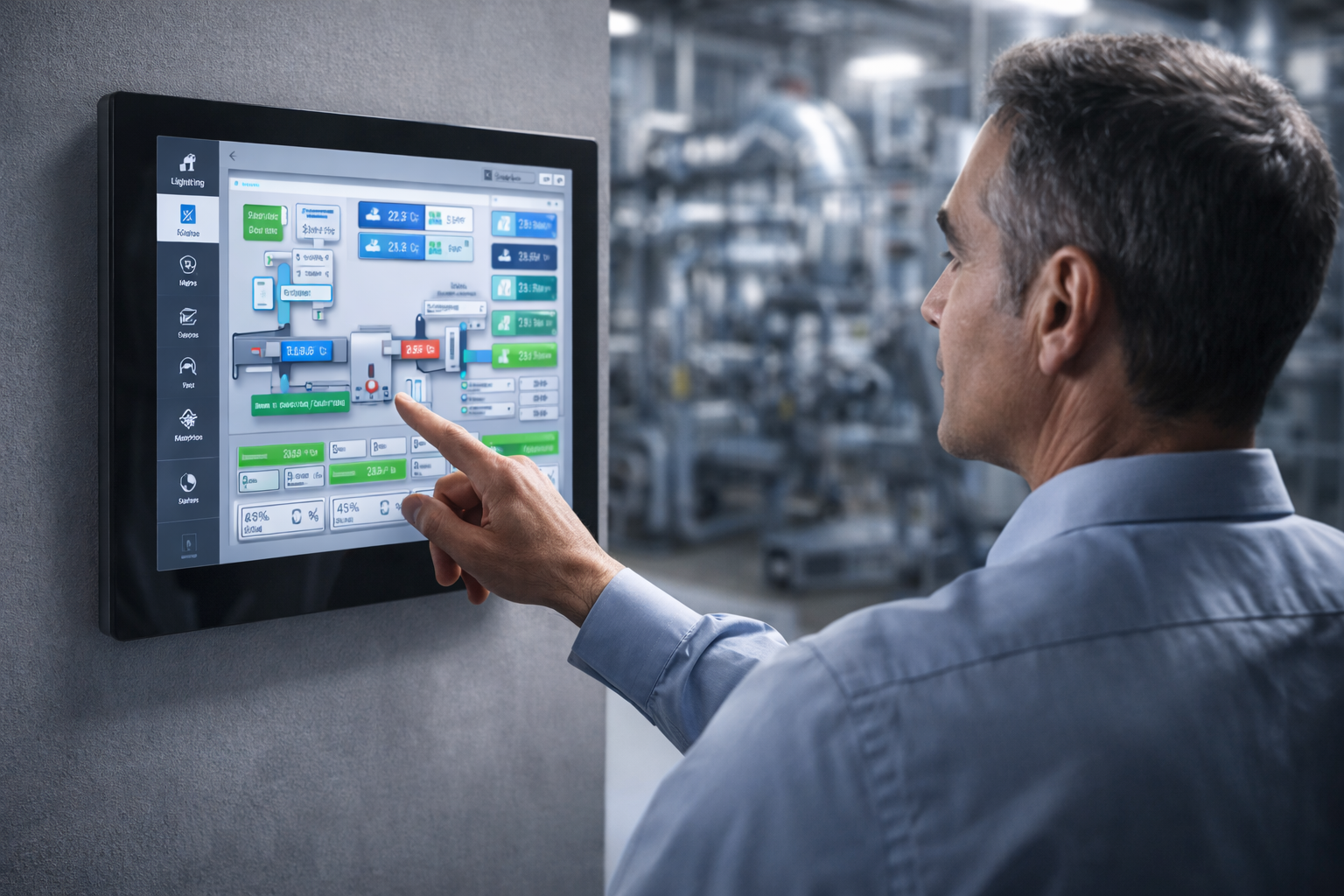
For Australian HVAC installers and facility managers, Belimo is synonymous with reliability. Whether you are fitting out a new commercial tower in Sydney or retrofitting a hospital plant room in Adelaide, you know that a Belimo orange actuator simply works.
However, the Belimo range is vast. Beyond the standard damper actuators, there are high-tech valves and safety solutions that can drastically reduce commissioning time and energy usage.
At Controls Traders, we warehouse a massive range of Belimo stock in South Australia, ready for fast delivery nationwide. Drawing on our 40 years of industry experience, here are the Top 5 Belimo products that every Australian installer should know about.
Safety is non-negotiable in Australian building codes. The Belimo LF Series is a staple for critical applications where a fail-safe position is required during a power outage.
When you need precise modulation for standard air handling, the NR Series is the industry workhorse. It is robust, easy to mount, and integrates seamlessly with almost any BMS.
This is the future of hydronic control. The Energy Valve is not just a valve; it is a 5-in-1 device combining a valve, actuator, flow sensor, and two temperature sensors.
In variable flow systems, pressure fluctuations can cause "ghost flows" and hunting. The Belimo PICV combines a differential pressure regulator with a control valve to maintain constant flow regardless of pressure changes.
Standard ball valves often have poor flow characteristics (a small opening lets through too much water). Belimo CCVs feature a specialized disc inside the ball port that ensures an "equal percentage" flow curve.
Whether you need the basic reliability of an NR24A-SR damper actuator or the advanced data analytics of an Energy Valve, choosing Belimo ensures you aren't returning to the site to replace failed gear in six months.
At Controls Traders, we are an Australian-owned business with deep stock levels of Belimo Actuators and valves in our Adelaide warehouse. We understand the local market and can help you cross-reference old part numbers to find the modern Belimo equivalent.
Read more
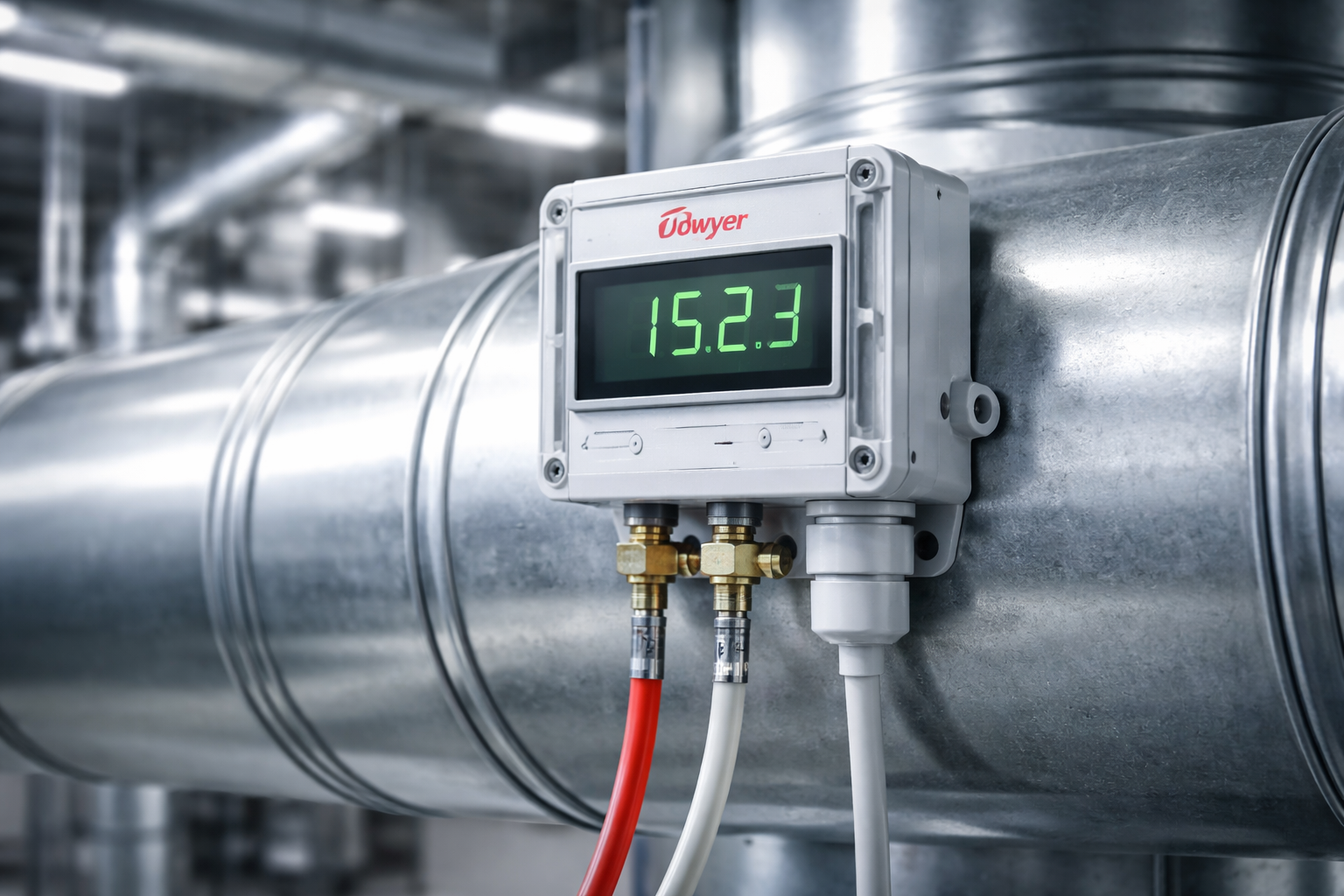

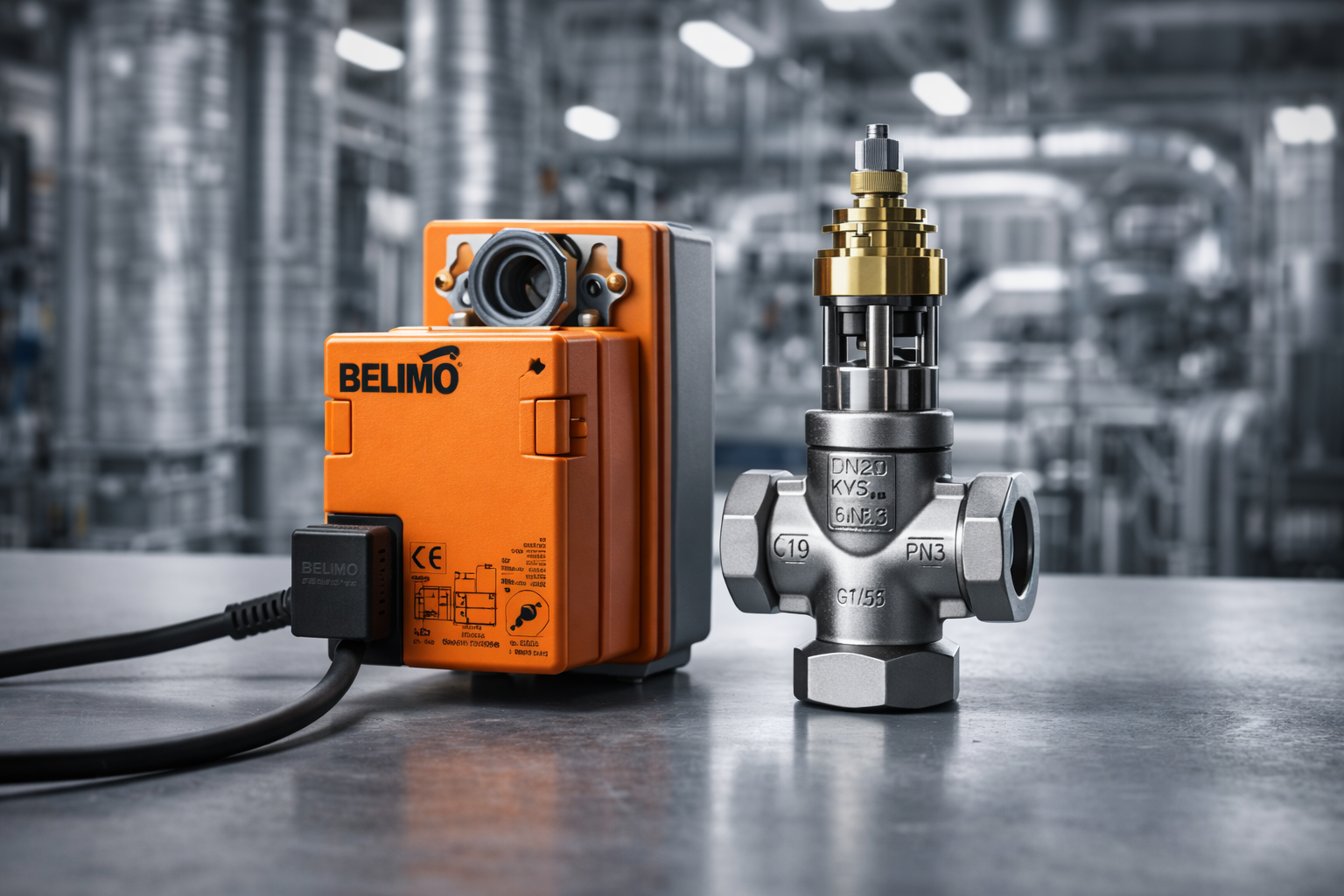
For HVAC installers and commissioning technicians, the differential pressure (DP) sensor is a critical component. Whether you are proving flow on a chiller or maintaining static pressure in a duct, you cannot commission a building without accurate pressure readings.
Finding these sensors in stock locally, however, can be a challenge. Waiting three weeks for a sensor to arrive from overseas often isn't an option when you have a handover deadline looming.
At Controls Traders, we warehouse a comprehensive range of [Differential Pressure Sensors] in Adelaide, ready for immediate dispatch across Australia. Here is what you need to know before you buy.
A differential pressure sensor measures the difference in pressure between two points in a system—the high side and the low side. It converts this mechanical difference into an electrical signal (typically 0-10V or 4-20mA) that your Building Management System (BMS) can read and act upon.
In modern HVAC, these sensors are the "eyes" of the system, allowing the BMS to modulate fans and pumps to match actual building demand rather than guessing.
When sourcing a sensor, you generally need to choose between two main categories:
We stock brands like Dwyer, BAPI, ACI, and Siemens that offer field-selectable ranges. This means you can buy one sensor and configure it for 0-250Pa or 0-500Pa on-site, saving you from carrying multiple part numbers in your van.
You will typically install these sensors for three main applications:
Before placing an order, check these three specs:
Supply chain delays are the enemy of profitable projects. Many suppliers list items online that are actually drop-shipped from Europe or the US, leading to unexpected delays.
At Controls Traders, we warehouse our stock locally in South Australia. This "convenience factor" means you don't have to wait for international freight. If a sensor fails on a critical site, you need a replacement in days, not weeks.
You can purchase high-quality sensors directly from Controls Traders. We are an Australian-owned business based in Stepney, South Australia.
Don't let a missing sensor hold up practical completion. Whether you need a simple switch for a filter or a high-precision transducer for a lab, buying from a local supplier ensures you get the right part, right now.
Read more
For HVAC consultants and commissioning engineers, hydraulic instability is the enemy of efficiency. In a traditional variable volume system, pressure fluctuations caused by opening and closing valves elsewhere in the loop can cause "ghost flows" and overflow conditions.
The solution to this hydraulic cross-talk is the Pressure-Independent Control Valve (PICV).
At Controls Traders, we have over 40 years of industry experience supplying high-performance valves to the Australian market. We see PICVs as the standard for modern energy-efficient design, replacing the traditional "control valve plus balancing valve" setup.
A PICV is a single valve body that combines three functions:
Unlike a standard control valve, where flow is a function of both opening area and differential pressure ($Q = Kv \times \sqrt{\Delta P}$), a PICV maintains a constant flow rate regardless of pressure changes in the branch line.
In a large chilled water system, when a valve closes on the ground floor, the pump pressure (head) increases for the rest of the building. In a standard system, this pressure spike forces more water through open valves on the top floor, leading to overflow and Low $\Delta T$ Syndrome.
A PICV prevents this using an internal mechanical regulator (often a diaphragm and spring).
This ensures that the control valve cone (the part the actuator moves) always sees a constant differential pressure, making the flow dependent only on the actuator position, not the pump speed.
When specifying or installing a PICV, you are dealing with three distinct elements:
Why are consultants specifying PICVs for hospitals and Green Star buildings?
Advanced Tech: For the ultimate in visibility, the Belimo Energy Valve combines a PICV with flow sensors and temperature sensors to measure energy consumption ($kWh$) and self-optimize based on real-time coil performance.
PICVs are the "go-to" solution for variable flow systems where efficiency is critical.
Scenario: A 10-story office building in Adelaide. The Problem: When the morning warmup sequence ends and VAV boxes throttle down, the pressure in the riser spikes. The PICV Solution: Instead of installing a 2-way ball valve and a manual balancing valve at every FCU, the installer fits a single Pressure Independent Control Valve.
The Pressure-Independent Control Valve is not just a valve; it is a hydraulic stabiliser. It decouples the control loop from the hydraulic loop, allowing your BMS to control temperature without fighting system pressure.
At Controls Traders, we stock a wide range of PICVs and matching actuators from brands like Belimo and Siemens. Whether you are retrofitting a plant room or designing a new build, getting the valve selection right is the first step to a high-efficiency building.
Read the full guide on our website for flow diagrams and actuator pairing charts.
Read more
Sign up by email to receive inspiration, product updates and special offers from our team.
 ACS Supplies
ACS Supplies
Welcome to our website. If you continue to browse and use this website, you are agreeing to comply with and be bound by the following terms and conditions of use, which together with our privacy policy govern Controls Traders Pty Ltd’s relationship with you in relation to this website. If you disagree with any part of these terms and conditions, please do not use our website.
The term ‘Controls Traders Pty Ltd’ or ‘us’ or ‘we’ refers to the owner of the website whose registered office is 40 Stepney Street, STEPNEY SA 5069. Our ABN is 21 610 375 365. The term ‘you’ refers to the user or viewer of our website.
The use of this website is subject to the following terms of use:
This privacy policy sets out how we uses and protects any information that you give us when you use this website.
We are committed to ensuring that your privacy is protected. Should we ask you to provide certain information by which you can be identified when using this website, then you can be assured that it will only be used in accordance with this privacy statement.
We may change this policy from time to time by updating this page. You should check this page from time to time to ensure that you are happy with any changes.
What we collect
We may collect the following information:
What we do with the information we gather
We require this information to understand your needs and provide you with a better service, and in particular for the following reasons:
Security
We are committed to ensuring that your information is secure. In order to prevent unauthorised access or disclosure, we have put in place suitable physical, electronic and managerial procedures to safeguard and secure the information we collect online.
How we use cookies
A cookie is a small file which asks permission to be placed on your computer's hard drive. Once you agree, the file is added and the cookie helps analyse web traffic or lets you know when you visit a particular site. Cookies allow web applications to respond to you as an individual. The web application can tailor its operations to your needs, likes and dislikes by gathering and remembering information about your preferences.
We use traffic log cookies to identify which pages are being used. This helps us analyse data about webpage traffic and improve our website in order to tailor it to customer needs. We only use this information for statistical analysis purposes and then the data is removed from the system.
Overall, cookies help us provide you with a better website by enabling us to monitor which pages you find useful and which you do not. A cookie in no way gives us access to your computer or any information about you, other than the data you choose to share with us.
You can choose to accept or decline cookies. Most web browsers automatically accept cookies, but you can usually modify your browser setting to decline cookies if you prefer. This may prevent you from taking full advantage of the website.
Links to other websites
Our website may contain links to other websites of interest. However, once you have used these links to leave our site, you should note that we do not have any control over that other website. Therefore, we cannot be responsible for the protection and privacy of any information which you provide whilst visiting such sites and such sites are not governed by this privacy statement. You should exercise caution and look at the privacy statement applicable to the website in question.
Controlling your personal information
You may choose to restrict the collection or use of your personal information in the following ways:
We will not sell, distribute or lease your personal information to third parties unless we have your permission or are required by law to do so. We may use your personal information to send you promotional information about third parties which we think you may find interesting if you tell us that you wish this to happen.
If you believe that any information we are holding on you is incorrect or incomplete, please write to or email us as soon as possible at the above address. We will promptly correct any information found to be incorrect.